In 2018, the promulgation of the GDPR (The European General Data Protection Regulation) touched off
a wave of discussions on data privacy protection for the games going abroad. One year later, as a
developer, do you know about GDPR? Please review today's article.
What is GDPR?
The European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a new set of data protection rules designed
to strengthen and unify all personal data protection in the European Union. And at the same time
GDPR also regulates the use of personal data in the EU outside the EU.
By far, the GDPR is the most extensive and strictest global data privacy protection regulation. The
regulation came into effect on May 25, 2018.
GDPR applicable for:
Although GDPR is a law promulgated by the European Union, it is binding on companies worldwide. For
developers, as long as they meet any of the following characteristics, they should comply with the
GDPR:
(1) Acquisition of users in EU member states, including advertising
(2) Data server is deployed in EU member states
GDPR: "Toughest " Data Privacy Protection Act
From May 25, 2018, the GDPR took effect immediately without any authorized legislation. After taking
effect, every single GDPR violation will be subject to severe penalties of up to 20 million Euros or
4% of the global annual turnover of the previous year, whichever is higher.
In addition, the GDPR's fine rules also have a collective punishment. According to the GDPR, any
company may be responsible for mistakes made by third parties because of data supply relationships.
If any party in the supply chain violates the rules, it may involve other data participants are
punished. Therefore, the GDPR emphasizes that all parties are actively conducting due diligence and
supplier management.
GDPR requirements:
The GDPR Act puts forward new requirements for the process of user data collection and processing.
The main updates include:
Clear data collection: Organizations must use concise language when soliciting users' consent to
collect their personal data, do not allow default consent for data collection, and allow users to
easily cancel data authorization.
Record-keeping requirements: Data administrators and any outsourcers must identify themselves, why
they process the data, who will receive it, and how long the data will be stored. Written records of
their data processing activities must also be kept and provided to the data protection agency.
Respect the right of users to access and delete data: GDPR requires data administrators to ensure
that users can access and receive all data provided to third-party companies, and when required by
customers, all third parties involved in data sharing are required to delete the user's data that is
also called "the right to be forgotten."
Guarantee user's right to know about data leakage: The company must notify the regulatory
authorities and individuals affected by the violation of data violations within 72 hours of
discovery. At the same time, it is necessary to mitigate the security risks caused by
vulnerabilities by identifying vulnerabilities and developing vulnerability solutions.
GDPR Developer Guide
The GDPR puts forward higher requirements for the entire industry. Under such challenges and huge
risks of violations, many developers have doubts about how to establish themselves in the
high-yielding European market. AdTiming recommends that developers grasp the coexistence of risks
and opportunities, increase the awareness of overall user information protection, and adopt the
following best practices to win user trust:
1. Obtain the player's explicit consent to collect personal information and anonymize it. Do not
select it by default.
When the player enters the game for the first time, AdTiming recommends that developers pop up the
privacy authorization of privacy authorization, whether to use user information for
interest-oriented advertising, and explicitly obtain player consent. Otherwise they are not allowed
to continue the game. If you set options for privacy policy, please note that all options should be
set to unchecked by default.
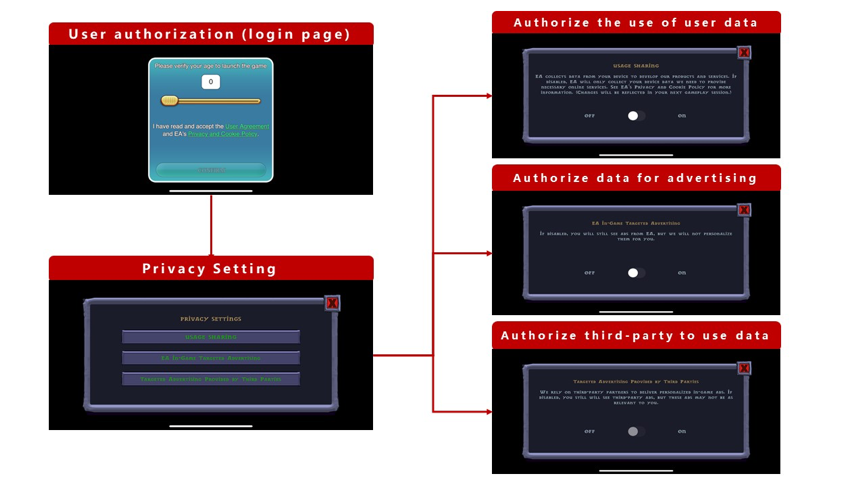 2. Display privacy policies
2. Display privacy policies
Secondly, in response to the requirements of GDPR, each game developer must formulate a new privacy
policy conforming to the provisions of GDPR, and disclose it to users and partners in a prominent
position, such as the first login page and the first login popup window of the company's official
website.

We recommend that developers comply with the GDPR policy when formulating their privacy policies,
follow the "minimization principle" and collect only game-based player data. At the same time, make
it clear to the player who they are, why the data should be processed, who will receive the data,
and how long the data will be stored, etc. The data must be deleted after the specified time.
3. Respect "the right to be forgotten" and provide players with a way to access, manage, and
delete personal data
A key part of the GDPR is that players can request gaming companies to access, manage, and delete
personal data. Therefore, in the design of game products, it is necessary to pay attention to adding
the right of players to access, manage, and delete data.
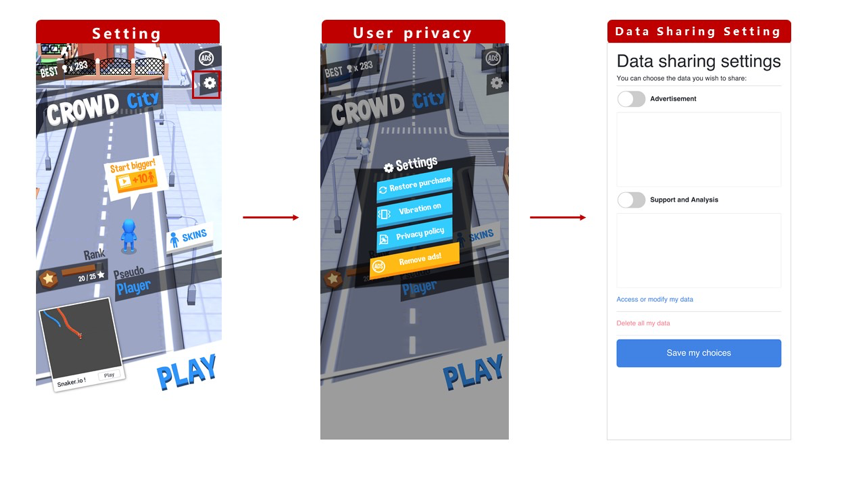
A more cautious approach is to set separate entrances on the game's main page to facilitate players'
management of personal data sharing permissions. Developers can also indicate in the privacy clause
that users can send emails to specific mailboxes to complete the deletion of personal data.
4. Review of GDPR compliance of third-party partners
Because of the GDPR's "collective punishment", developers are obliged to monitor the use of data by
third-party cooperation platforms that also comply with GDPR regulations. During the process, in
addition to viewing the other party's privacy protection regulations, you can also refer to the
IAB's Transparency & Consent Framework Global Vendor List, and only select those who comply with the
IAB framework agreement and are in the list of certified vendors. Companies to cooperate.
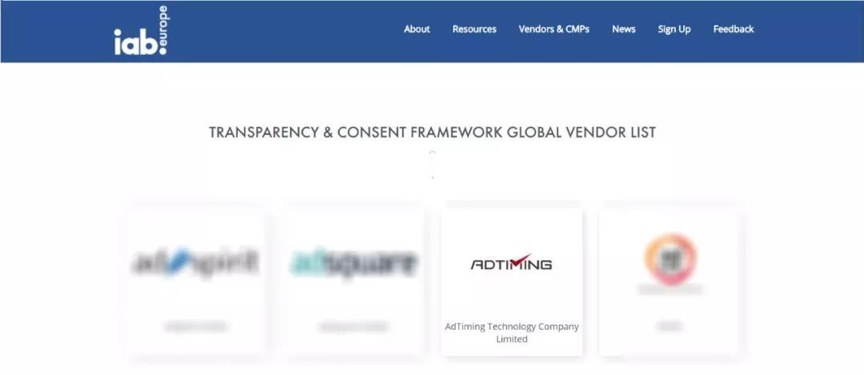
This framework was proposed by the IAB (Interactive Advertising Bureau), which sets standards for
the process of obtaining user data processing and disseminating such information in the advertising
supply chain. The companies in this framework provider list ensure that they obtain user permissions
when participating in digital advertising and that they comply with GDPR's privacy policy provisions
when processing personal or non-personal data on user devices.
5. Cooperate with third-party platform to authorize data use
As part of the developer's business ecosystem, third-party platforms, including AdTiming, will not
directly participate in the collection of user information collection, but will obtain user
authorization through the cooperation of developers in subsequent cooperation.
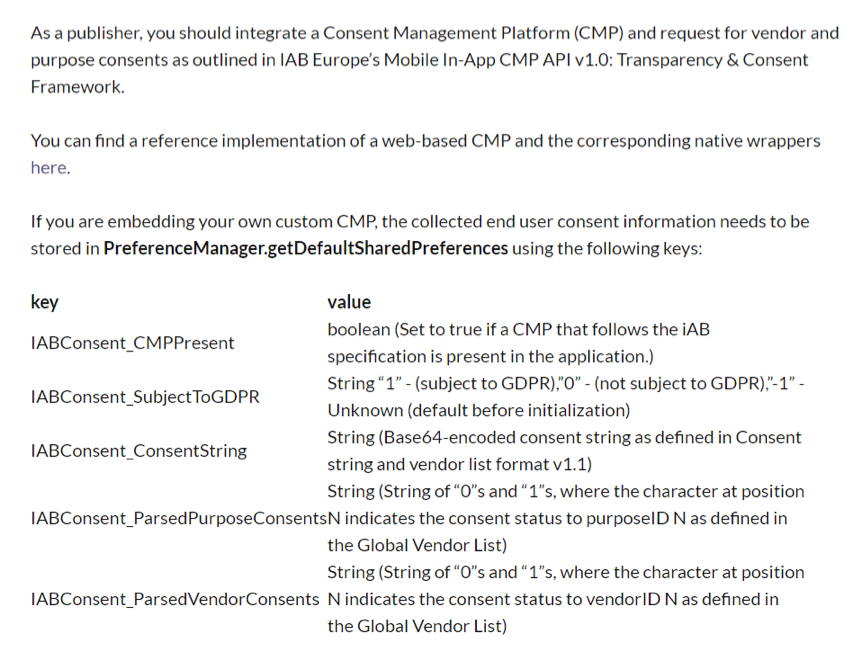
Taking the AdTiming SDK as an example, when integrating the AdTiming SDK, we recommend that
developers follow the following steps to pass the consent of anonymous users for information
collection consent in the form of code parameters to the AdTiming platform to complete the
authorization.


 2. Display privacy policies
2. Display privacy policies We recommend that developers comply with the GDPR policy when formulating their privacy policies,
follow the "minimization principle" and collect only game-based player data. At the same time, make
it clear to the player who they are, why the data should be processed, who will receive the data,
and how long the data will be stored, etc. The data must be deleted after the specified time.
We recommend that developers comply with the GDPR policy when formulating their privacy policies,
follow the "minimization principle" and collect only game-based player data. At the same time, make
it clear to the player who they are, why the data should be processed, who will receive the data,
and how long the data will be stored, etc. The data must be deleted after the specified time.
 A more cautious approach is to set separate entrances on the game's main page to facilitate players'
management of personal data sharing permissions. Developers can also indicate in the privacy clause
that users can send emails to specific mailboxes to complete the deletion of personal data.
A more cautious approach is to set separate entrances on the game's main page to facilitate players'
management of personal data sharing permissions. Developers can also indicate in the privacy clause
that users can send emails to specific mailboxes to complete the deletion of personal data.
 This framework was proposed by the IAB (Interactive Advertising Bureau), which sets standards for
the process of obtaining user data processing and disseminating such information in the advertising
supply chain. The companies in this framework provider list ensure that they obtain user permissions
when participating in digital advertising and that they comply with GDPR's privacy policy provisions
when processing personal or non-personal data on user devices.
This framework was proposed by the IAB (Interactive Advertising Bureau), which sets standards for
the process of obtaining user data processing and disseminating such information in the advertising
supply chain. The companies in this framework provider list ensure that they obtain user permissions
when participating in digital advertising and that they comply with GDPR's privacy policy provisions
when processing personal or non-personal data on user devices.

